?What Is Fiber Optics
Fiber optics is the technology used to transmit information as pulses of light through strands of fiber made of glass or plastic over long distances.
Optical fibers are about the diameter of a strand of human hair and when bundled into a fiber-optic cable, they’re capable of transmitting more data over longer distances and faster than other mediums. It is this technology that provides homes and businesses with fiber-optic internet, phone and TV services.
Fiber optic cables
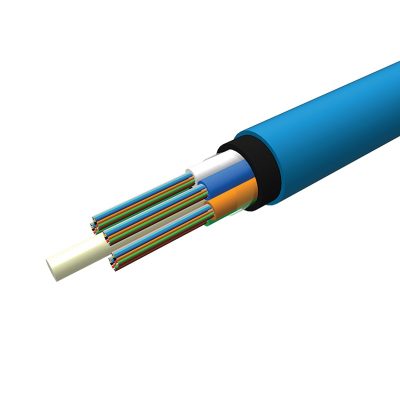
A fiber-optic cable contains anywhere from a few to hundreds of optical fibers within a plastic casing. Also known as optic cables or optical fiber cables, they transfer data signals in the form of light and travel hundreds of miles significantly faster than those used in traditional electrical cables. And because fiber-optic cables are non-metallic, they are not affected by electromagnetic interference (i.e. weather) that can reduce speed of transmission. Fiber cables are also safer as they do not carry a current and therefore cannot generate a spark.
What is a fiber-optic network?
There are several different types of fiber-optic networks but they all begin with optic cables running from the network hub to the curb near your home or straight to your home to provide a fiber-optic internet connection. The fastest type of fiber network is called Fiber to the Home (FTTH) or Fiber to the Premises (FTTP) because it’s a 100% fiber-optic connection with optical fiber cables installed to terminals directly connected to houses, apartment buildings and businesses.
On the other hand, Fiber to the Curb (FTTC) is a partial fiber connection because the optical cables run to the curb near homes and businesses and copper cables carry the signals from the curb the rest of the way. Similarly, Fiber to the Building (FTTB) is when fiber cable goes to a point on a shared property and the other cabling provides the connection to offices or other spaces.
Fiber-optic internet
Now that you know how fiber optics work, let’s talk about the many benefits of fiber-optic speed. When you’re on a FTTH network, you’ll experience significantly faster upload and download speeds, more bandwidth for multiple devices at home and a reliable connection. And that’s exactly what you’ll get with Verizon Fios, the 100% fiber-optic network.
types of fiber optic cable commonly used
There are three types of fiber optic cable commonly used: single mode, multimode and plastic optical fiber (POF).
Transparent glass or plastic fibers which allow light to be guided from one end to the other with minimal loss.
Fiber optic cable functions as a “light guide,” guiding the light introduced at one end of the cable through to the other end. The light source can either be a light-emitting diode (LED)) or a laser.
The light source is pulsed on and off, and a light-sensitive receiver on the other end of the cable converts the pulses back into the digital ones and zeros of the original signal. Even laser light shining through a fiber optic cable is subject to loss of strength, primarily through dispersion and scattering of the light, within the cable itself. The faster the laser fluctuates, the greater the risk of dispersion. Light strengtheners, called repeaters, may be necessary to refresh the signal in certain applications.
While fiber optic cable itself has become cheaper over time – a equivalent length of copper cable cost less per foot but not in capacity. Fiber optic cable connectors and the equipment needed to install them are still more expensive than their copper counterparts.
Single Mode cable is a single stand (most applications use 2 fibers) of glass fiber with a diameter of 8.3 to 10 microns that has one mode of transmission. Single Mode Fiber with a relatively narrow diameter, through which only one mode will propagate typically 1310 or 1550nm. Carries higher bandwidth than multimode fiber, but requires a light source with a narrow spectral width. Synonyms mono-mode optical fiber, single-mode fiber, single-mode optical waveguide, uni-mode fiber.
Single Modem fiber is used in many applications where data is sent at multi-frequency (WDM Wave-Division-Multiplexing) so only one cable is needed – (single-mode on one single fiber)
Single-mode fiber gives you a higher transmission rate and up to 50 times more distance than multimode, but it also costs more. Single-mode fiber has a much smaller core than multimode. The small core and single light-wave virtually eliminate any distortion that could result from overlapping light pulses, providing the least signal attenuation and the highest transmission speeds of any fiber cable type.
Single-mode optical fiber is an optical fiber in which only the lowest order bound mode can propagate at the wavelength of interest typically 1300 to 1320nm.
Multi-Mode cable has a little bit bigger diameter, with a common diameters in the 50-to-100 micron range for the light carry component (in the US the most common size is 62.5um). Most applications in which Multi-mode fiber is used, 2 fibers are used (WDM is not normally used on multi-mode fiber). POF is a newer plastic-based cable which promises performance similar to glass cable on very short runs, but at a lower cost.
Multimode fiber gives you high bandwidth at high speeds (10 to 100MBS – Gigabit to 275m to 2km) over medium distances. Light waves are dispersed into numerous paths, or modes, as they travel through the cable’s core typically 850 or 1300nm. Typical multimode fiber core diameters are 50, 62.5, and 100 micrometers. However, in long cable runs (greater than 3000 feet [914.4 meters), multiple paths of light can cause signal distortion at the receiving end, resulting in an unclear and incomplete data transmission so designers now call for single mode fiber in new applications using Gigabit and beyond.
BASIC CABLE DESIGN
Loose-tube cable, used in the majority of outside-plant installations in North America, and tight-buffered cable, primarily used inside buildings.The modular design of loose-tube cables typically holds up to 12 fibers per buffer tube with a maximum per cable fiber count of more than 200 fibers. Loose-tube cables can be all-dielectric or optionally armored. The modular buffer-tube design permits easy drop-off of groups of fibers at intermediate points, without interfering with other protected buffer tubes being routed to other locations. The loose-tube design also helps in the identification and administration of fibers in the system.
Single-fiber tight-buffered cables are used as pigtails, patch cords and jumpers to terminate loose-tube cables directly into opto-electronic transmitters, receivers and other active and passive components. Multi-fiber tight-buffered cables also are available and are used primarily for alternative routing and handling flexibility and ease within buildings.
Loose-Tube Cable
In a loose-tube cable design, color-coded plastic buffer tubes house and protect optical fibers. A gel filling compound impedes water penetration. Excess fiber length (relative to buffer tube length) insulates fibers from stresses of installation and environmental loading. Buffer tubes are stranded around a dielectric or steel central member, which serves as an anti-buckling element.
The cable core, typically uses aramid yarn, as the primary tensile strength member. The outer polyethylene jacket is extruded over the core. If armoring is required, a corrugated steel tape is formed around a single jacketed cable with an additional jacket extruded over the armor.
Loose-tube cables typically are used for outside-plant installation in aerial, duct and direct-buried applications.
Tight-Buffered Cable
With tight-buffered cable designs, the buffering material is in direct contact with the fiber. This design is suited for “jumper cables” which connect outside plant cables to terminal equipment, and also for linking various devices in a premises network.
Multi-fiber, tight-buffered cables often are used for intra-building, risers, general building and plenum applications.
The tight-buffered design provides a rugged cable structure to protect individual fibers during handling, routing and connectorization. Yarn strength members keep the tensile load away from the fiber.
As with loose-tube cables, optical specifications for tight-buffered cables also should include the maximum performance of all fibers over the operating temperature range and life of the cable. Averages should not be acceptable.
Source:
Related products...
fiber-optic-cable
Rafsanjan 6-core fiber optic cable, multimode (6 * 1), OFC, SJ
fiber-optic-cable
fiber-optic-cable
12-core OBUC (2×6), single-mode NZDSF, PBN brand dry fiber optic cable



















[ratings]