RoCE vs Infiniband vs TCP/IP
As is well-known, a network protocol is a set of rules governing how data is exchanged in the network. Well, Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and TCP/IP network protocols are usually used in distributed storage networks. Typically, there are three types of RDMA: RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE), Infiniband, and Internet Wide Area RDMA Protocol (IWARP). So, what are they and which is the most suitable one for data centers?
What Is RoCE?
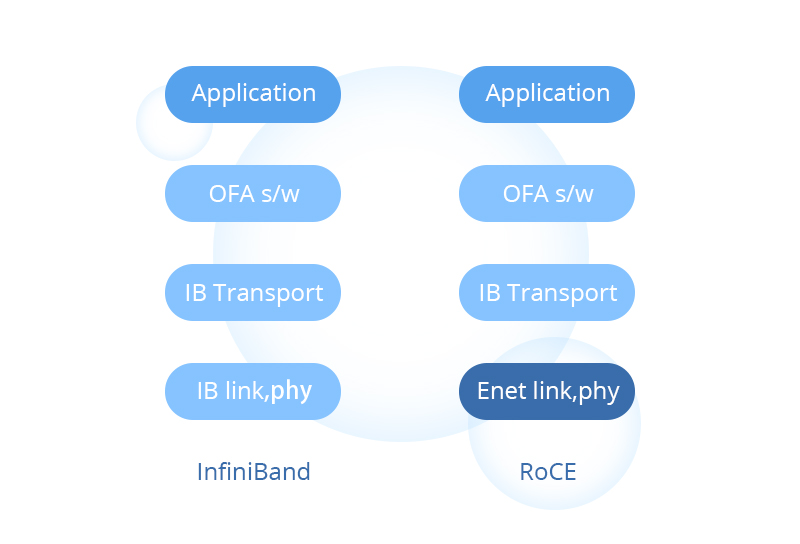
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is a network protocol defined by the InfiniBand Trade Association(IBTA) standard, which allows data to transfer from one machine to another with much less work being done by the CPU. Generally, there are two main versions of RoCE: RoCEv1 and RoCEv2. RoCE v1 is an Ethernet link layer protocol, while RoCE v2 is an internet layer protocol.
RoCE achieves lower latency than its predecessor, the IWARP protocol. In addition, the advantages of RoCE, such as high cost-efficiency, high performance, and low power consumption, can bring many benefits to modern commercial data centers. It is especially suitable for performance-sensitive or cost-constrained computing environments, such as cloud computing.
What Is Infiniband?
Infiniband is a new generation network protocol that supports RDMA, which is used in high-performance computing. It has extremely high throughput and low latency, usually used for data interconnection between computers, servers or storage systems.
Different from RoCE, Infiniband performs RMDA over Infiniband adapters or switches instead of Ethernet. Therefore, Infiniband can achieve lower latency and higher bandwidth than RoCE. A specific type of Ethernet switch has port-to-port latency of 230 ns, while an InfiniBand switch with the same number of ports has 100 ns. However, Infiniband is also more expensive because IB NICs and switches must be supported.
What Is TCP/IP?
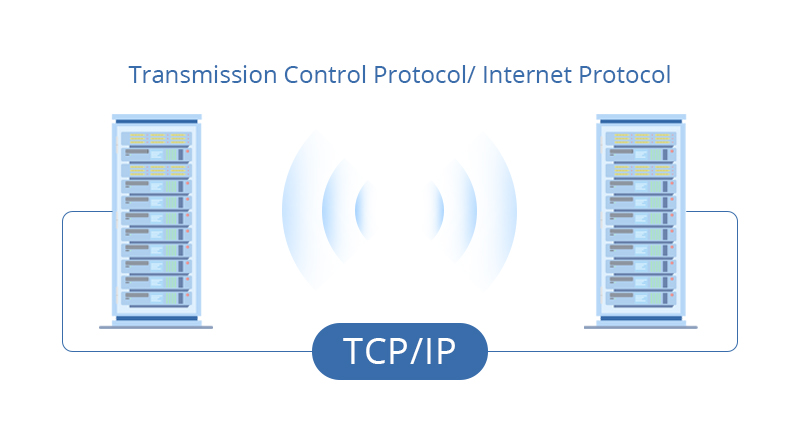
TCP/TP, or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, is used to interconnect network devices over the Internet. It identifies how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed, and received. TCP/IP places lots of emphasis on accurate data transmission between two computers. If the system encountered some problem while sending the message in one go, the entire message must be sent again.
In addition, the functionality of TCP/IP divides into four different layers: datalink layer, internet layer, transport layer, and application layer. Data must go through these four layers before being received at the other end. Then, TCP/IP will reassemble the data by passing the layers in the opposite order and present it to the receivers. In this way, you can improve the performance or security of data centers by upgrading certain layers rather than the whole system.
RoCE vs Infiniband vs TCP/IP
As mentioned above, RoCE and Infiniband are two common network protocols of RDMA technology. Compared to TCP/IP, RDMA has direct access to memory data via network interface rather than through the kernel, enabling low-latency and high-performance transmission. These three network protocols are different from each other in several respects.
- High Scalability: All these three network protocols have high scalability and flexibility, with Infiniband being the most scalable. A single subnet of Infiniband can support tens of thousands of nodes. Besides, it also provides relatively simple and scalable architecture, creating almost unlimited cluster sizes through Infiniband routers.
- High performance: Since TCP/IP burdens CPU processing resources and latency, it performs worse compared to the other two network protocols. And RoCE increases speed and power in enterprise data centers while reducing total cost of ownership without replacing Ethernet infrastructure. As for Infiniband, it uses serial links and buses to send data one bit at a time, enabling faster, more efficient communications.
- Easy management: Although RoCE and Infiniband have lower latency and higher performance than TCP/IP, the latter is easier to deploy and manage. The network administrators who use TCP/IP to build up devices and network connectivity only need little central management.
- Cost-efficiency: For enterprise data centers with limited budget, Infiniband is probably not a good choice. It uses expensive IB switching ports to carry a large number of applications, increasing the computing cost, maintenance cost, and management cost of enterprises. In contrast, RoCE and TCP/IP using ethernet switches are more cost-effective.
- Network devices: As the table shows below, both RoCE and TCP/IP achieve data transmission through ethernet switches, while Infiniband uses IB switches with independent architecture to carry applications. Typically, IB switches must be interconnected with devices that support IB protocol and are relatively closed and difficult to replace.
Source: community.fs
Related products...
fiber-optic-cable
fiber-optic-cable
fiber-optic-cable
LEONI fiber optic cable 6 core (6*1), multimode, MM 50، In/Out-LSZH















[ratings]